Ever since I read Influence: The Psychology of Persuasion by Robert Cialdini I became fascinated with human behavior. Understanding how rules of Reciprocity, Scarcity or Authority work has benefited me immensely. First of all, you begin to understand when others try to influence your decision. Second of all, you can use the same techniques to influence the decisions of others.
Cialdini was one of the first people to focus and write a book for the general population on this topic. Since then we have gone a long way and identified more psychological principles that run our lives.
These findings are particularly prominent in marketing for eCommerce and SaaS businesses. Psychology has helped many businesses to grow, one of the best examples of this is booking.com. They use almost all of the principles listed below to influence users behavior and thanks to Conversion Rate Optimization other businesses can also benefit from the learning of psychology.
In the following article, we’ll go through the principles that can help you influence consumer behavior, optimize campaigns, create new user flows and write better copy.
Speak-easy effect
We find familiar things easier to process and understand than the unfamiliar. So things that are easier to read and say are perceived as more trustworthy and valuable.
The speak-easy effect means using simple language instead of difficult words on your website. It allows people to feel more comfortable and trustworthy.
The secret to having the attention of your users is avoiding elaborated sentences or uncommon words. In one of the famous case studies of this effect participants rated food additives as more harmful when their names were more difficult to pronounce. This proves that words that are easier to understand are perceived as more trust.
A master in this area is Apple. They always manage to explain a complicated topic with words easily understandable.
Priming
Priming is a complex process that impacts a significant part of our behavior. It is driven by the subconscious mind and it works by activating an unnoticeable association in the users’ short-term memory towards a second stimulus.
The uses of priming in a digital marketing can be endless.You can prime your customers using visuals, music, elements of your website or even words.
A great example of this for eCommerce is showing the coupon field by default in the checkout. When you expose the customer to an open coupon field they are more likely to search for a coupon. This is a very good example of priming. We have shown the user that there is a coupon available thus making him look for a cheaper option.
Choice paradox
Giving users more options makes it harder for them to make a decision.
As humans we tend to resist situations where there are too many choices, the reason is that we have limited attention, and prefer minimalism when processing things for the first time.
In effect abundance instead of increasing customer happiness can heighten the expectations and create a fear of missing out.
A great example of this phenomenon is when you’re browsing Nextflix’s catalogue and you have so many options that you end up feeling overwhelmed and not choosing anything. Does it sound familiar to you?
As marketers we can mitigate this problem by emphasizing one choice over the others and avoid having many products with slight variations.
Social Proof
Consumers are influenced by the opinions of others.
When they are unsure about buying a product or service they look to other opinions and consider them for their final decision.
Social proof is a phenomenon when people are not sure how to act, they look to others for clues.
For example, if you are new in a city and you’re looking for something to eat or visit it’s more likely that you’ll enter a place that is full of people than another that is empty.
Also, people have a desire to fit in with the rest of the crowd so this influences many aspects of their lives, including purchasing behavior.
Let’s see some interesting statistic facts:
- 61% of customers read online reviews before choosing to buy a product or service
- 91% of 18-34-year-olds trust online social proof reviews as much as recommendations from someone close to them.
- 63% of consumers indicated they are more likely to purchase from a website with product ratings and reviews.
In digital marketing, we can incorporate social proof to influence decisions. Here are some examples of Social proof:
Booking.com uses testimonials and information about how many people view/book the same property to build social proof.
Framing
Framing is when our decisions are influenced by the way information is presented.
Similar information can be more positive or negative depending on the features that are highlighted. For example, people tend to have different behavior depending if something is framed as “gain” (you could have) or “loss” (don´t miss out). This is because consumers avoid risks when presented with gain frames and seek chances when faced with a loss frame.
Another example marketers can use is that people tend to choose options that have higher numbers, as our bias believes that higher is better.
Framing can affect behavior so, it’s essential to understand how we can use it to be more influential when talking to potential customers.
1.Visual frames
Visual frames are related to factors such as color, font size, font style, or even body language all these play a huge role in getting the attention of potential clients and persuade them to make a purchase.
2. Value frames
Value frames are used to make us feel that we are getting a better deal or offer than we really are. Higher numbers tend to mean better value. For example getting $120 off instead of 20% discount.
3.Positive and negative frames
When you make people feel like they are losing something, people tend to fear and take action to avoid losses. So when we may lose out on a good deal, we are encouraged to take action.

Hick´s Law
The principal idea of Hick’s law is that the more choices available, the more time users take to make their decisions.
In life and in work it’s always recommendable to keep things simple. This also applies to UX design.
For a marketer and a designer it’s essential to know Hick’s Law. With this in mind you can examine how many options you give the user and how it affects the decision-making process.
If you look around you’ll find many other examples of Hick’s Law. For example, in a menu at a restaurant. Having a limited choice can be a good thing, because customers will make a decision faster. If your business is all about turnover you should think about carrying a selected but limited inventory.
However, this law doesn’t apply to every situation, especially the ones that need deep analysis. When there is a lot of different factors to examine and take into consideration the decision process is long by default and Hick’s law does not affect the decision as strongly.

Zeigarnik effect
Our brain is programmed to remember incomplete or interrupted actions more.
Imagine this – you leave work just before sending the last important email and you keep it on your mind until you finally click send. Problems like this, that aren’t completed give us a sensation of stress. This is also the reason why we tend to think about things that still have to be done, but which we have been postponing for ages. In marketing this type of situation encourages customers to pursue certain actions.
For example, if you integrate the Zeigarnik effect into your website, you can ensure a longer browsing time on it. A great way of making this happen is showing percentages in certain processes such as registration, checkout or shipping process. When users move from one stage to another you should inform about progress to keep them engaged.

You can apply this principle also in news and blog posts by giving your readers an insight of the headline combined with a short teaser text, this will encourage them to keep reading.
Miller’s Law
An average person is capable of storing 5–9 elements in short-term memory.
The number varies depending on the kind of information required to memorize (sound, taste, image, number).
You can apply this law on your website by organizing your products in groups from 5 to 9 categories instead of listing all of them. This way you help your customers find what they need faster.
This is especially useful for new customers because it allows them to familiarize themselves with the structure and organization of the site.
Miller´s Law also highlights the importance of proper planning in the design process, because as you add more features to a product your interface must be able to accommodate those without modifying the visual foundation of what you built.
Another important thing to keep in mind next time you’re about to create a campaign or improve your website is that most successful tag-lines are never longer than seven words.
Confirmation Bias
We interpret things based on our preconceptions and we give more credit to information we believe in and ignore the one that we think is wrong.
The reason for this phenomenon is because the chemicals in our brain fabricate incoming data to intensify our perception of the world: emphasising supportive evidence and minimizing anything contrary.
A clear example of this is that people still buy supplements, even though studies have shown that they are useless because we have been told they are good for our health.
As marketers, we can benefit from this by pointing out our target’s beliefs around our products and services and then provide the evidence that confirms those beliefs. And once we’ve achieved a level of brand awareness, we can use confirmation bias to reinforce what consumers “already know” about us.
Cashless Effect
It has been proven that consumers are more willing to pay when there is no physical money involved in a transaction, this is called the Cashless effect.
Therefore, when users pay with a credit card it makes them feel more comfortable because they are actually not seeing the amount of money they are spending.
This effect occurs in any situation where digital forms of payment are used instead of cash. People tend to be much looser with their money when it only exists in a digital form, and often spend more money that they wouldn’t if they had to make the same transaction with physical cash.
Take the example of Apple & Amazon who have been capitalizing on the pain of paying by introducing new technologies such as Apple Pay, which involves Apple users simply waving their gadgets in order to pay for purchases and Amazon’s patented “1 click ordering” technology.
Von Restorff Effect
When multiple similar objects are present, the one that differs from the rest is most likely to be remembered, this phenomenon is called the Restorff Effect.
For example, in a list of images that have similar characteristics (size or color) except for one that is notably different, users’ will notice this one and remember it more clearly.
Von Restorff effect shows how human eyes and brains are constantly on the lookout for things that disrupt the norm so it can be applied to all things (words, products or messages.
In the context of eCommerce this is the main reason why all call-to-actions look different from the rest of the action buttons on a site. This is also the reason, we remember bold words more, or if that CAPITALIZED words stand out inside a phrase.
To make use of this effect in eCommerce we can for example include a banner inside a list of products at the same time providing a different background or product photo to an item we really want to push out is a good strategy.
Curiosity Gap
This principle refers to the discrepancy between what we currently know and what we would like to know.
Curiosity Gap it’s a powerful copywriting technique used to create irresistible headlines that catch users’ attention and makes them click to see the rest of the content.
Please keep in mind, when you use this technique for headlines, it needs to be specific enough to entice the reader, but not so specific that the reader doesn’t need to click through.
Media websites such as BuzzFeed or Upworthy are great examples of using the Curiosity Gap. Sometime this effect may seem as a manipulation to get high click-through rates, but so do other psychological principles. The best way to defend against it, is to understand the underlying principles behind it. In the end, it’s recommended to use this method with moderation.
Halo Effect
Occurs when the first positive impression of a person or brand influences the overall perception of the person or brand.
When consumers have positive experiences with a specific product they cognitively form an assumption about the whole brand. The explanation of this is that subconsciously a person assumes that if a company is exceptionally good at one thing, they will undoubtedly be good at something else.
The halo effect increases brand loyalty, strengthens the brand image and reputation, and translates into high brand equity. In marketing it is a great technique to establish leadership in the industry. When one product positively imprints in the minds of consumers, the success of that product infectiously affects other products.
A clear example of the Halo Effect is again, Apple. The success of the Ipod allowed the company to successfully launch products such as the Apple Watch, iPhone, and iPad.

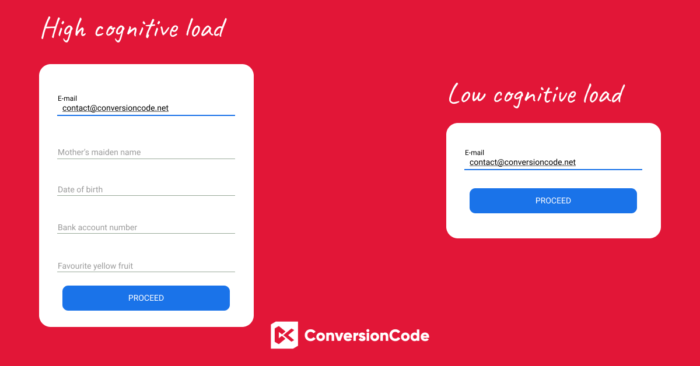
Cognitive load
The total amount of mental effort that is required to complete a task is called the Cognitive Load.
As marketers we can use this theory to figure out the best way to feed information to our potential customers. You can think of it as the processing power needed by the user to interact with your website. If the information that needs to be processed is too difficult the cognitive load will be too high. This means that to improve UX present less information or present it in chunks, so you can ensure it can be easily understood. Whether it’s a blog, an ebook or a landing page, make sure it’s easy to navigate and process.
When you need to explain complex ideas, create short sentences, multiple subheaders, bullet points, and use videos and images to support your ideas.
In addition you can also use tools to help your user’s memory such as checklists, glossaries, quick reference guides, or diagrams. Avoid trying to cover too much ground when you’re writing about a topic. The same goes for multiple call to action buttons. If you ask too much from your potential customers you might get nothing in return.
Reciprocity
Human nature wants to offer something in exchange when something is received.
When you give a product or service for free, people feel a real sense of indebtedness towards you.
A great example of reciprocity are free trials. Spotify has mastered this with its Premium membership, the ingenious thing about it is that you begin to integrate this service into your daily life, such that when the trial ends, you feel the need of having the service permanently.
In addition another important thing to consider is that there are two types of reciprocity: material and emotional. Although businesses often use material incentives for reciprocation, emotional reciprocation offers a great customer experience and it also makes them feel more valuable.
Bringing It All Together
I strongly believe in using psychology in marketing. As mentioned at the start, the first way to defend against psychology is understanding it. When you finally get a grasp of this, you can start using it yourself.
If you liked the article, I would be really if you’d subscribe to my newsletter. I send out monthly tips and tricks regarding digital marketing, analytics and CRO.

